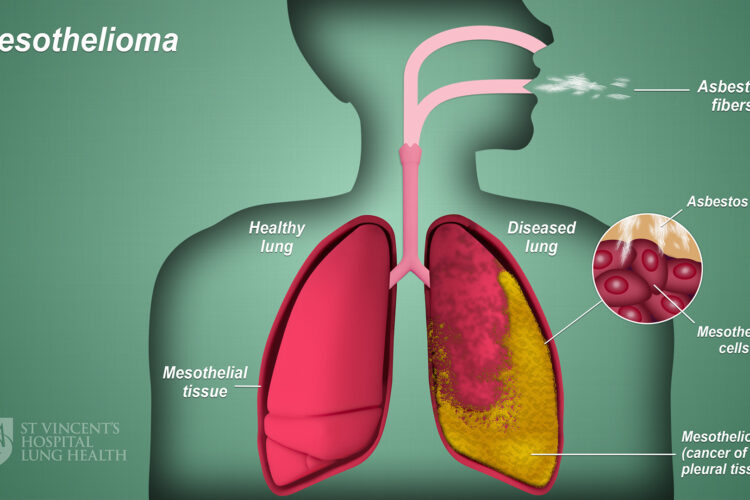
Mesothelioma is a rare type of cancer in which malignant (cancerous) cells are found in the mesothelium, which surrounds most of the body’s internal organs. Most people with this cancer have had some significant asbestos exposure.
Patients can be without symptoms for upwards of twenty to fifty years. When a diagnosis is made, the cancer has already become too advanced. The triggers and mechanisms that cause this form of cancer have been recently uncovered, and as a result, new treatment modalities are being formed and assessed.
According to Cancer Research, approximately 2700 new mesothelioma cases are diagnosed in the UK yearly. The disease seems to affect men more than women. The disease isn’t sex-specific, and the predominant male infection rate is directly linked to their more significant numbers in the workforce.
The Unseen Danger
Asbestos, a silicate, was used mainly as an insulation material for buildings, tiles, ships, plumbing, and factories in the early 20th century. It causes most of all mesotheliomas.
The danger of asbestos lies in its removal, usually during demolition or renovation work. Therefore, it is vital to get a professional asbestos risk assessment company such as AJC Environmental to check for asbestos before work begins. Small particles or fibres go into the air and are inhaled. The fibres can get lodged in the throat, trachea, and bronchi. The thinner particles can reach the lung and chest cavity and once lodged, affect the mesothelial cells. These cells line the significant organs and form the outer lining of the body’s serous cavities.
The asbestos starts causing minute cellular changes in the mesothelium, followed by small cancer and tumour growth. In advanced stages, it’s thought that the cancer cells travel by the lymphatic system to other organ systems in the body. The most common site for mesothelioma is in the pleural cavity and lungs. It can also occur in the stomach and throat.
The chances of acquiring this disease are linked to the time and amount of asbestos exposure. In addition, smokers with asbestos exposure double their risk of getting Mesothelioma versus non-smokers.
Get Diagnosed Early
When symptoms do appear, the patient usually complains of wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, pain in the chest and fluid in the lungs. As the cancer progresses, abdominal masses, abdominal pain, weight loss and irregularities in bowel function are a few of the symptoms that can occur.
Diagnosis is first made by taking an extensive medical history and assessing asbestos exposure. This, in turn, is followed with a chest X-Ray, MRI or CAT Scan. If Mesothelioma is suspected, a biopsy must be done to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment success, as with all cancers, relies on an early diagnosis. Unfortunately, as mentioned before, symptoms start occurring when the cancer has already reached a more advanced stage. Classification of Mesothelioma is like other cancers, with four stages. Stage 1, which is early, tends to be the most successfully treated. Stages 2, 3 and 4 are much more challenging to deal with. Traditional treatments being used by oncologists today are a combination of surgery, radiation treatment and chemotherapy. Some other experimental treatment options include drug therapy, gene therapy, immunotherapy, and photodynamic therapy.
Possible Breakthroughs Ahead
However, the mechanism by which asbestos causes cancer has recently been discovered. Scientists now know that once asbestos encounters the mesothelium, it causes the release of an enzyme called TNF-alpha, which starts biochemical changes within the cells. These changes lead to the formation of a protein, which protects the cancer cell against death. As these cells multiply, more damaged cells form, eventually causing cancer. As a result of this knowledge, a new drug developed by Alfacell, is currently in clinical trials. The drug Onconase works by stopping the damaged cells from replicating. This slows cancer growth and helps to shrink the tumours. Tests so far are quite promising. It’s hoped that it will help those in the advanced stages of Mesothelioma to survive longer and that it could reverse the cancer in Stage 1 patients.
Hopefully, with this added knowledge, more drugs will be developed and evaluated, eventually leading to this devastating disease’s eventual cure.