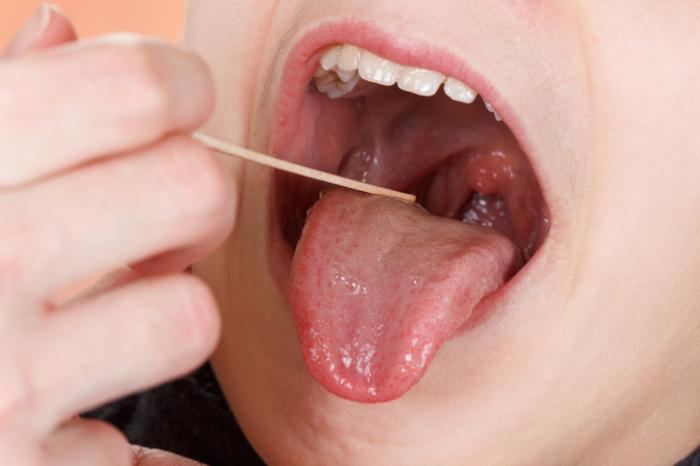
Strep throat or tonsillitis may produce a chronic soreness in the back of the throat that persists despite frequent brushing and flossing, as well as poor breath (an infection of the tonsils). If you have yellow-white masses in addition to your tonsil pimples, you are more likely to have tonsil stones. But do you really think are tonsil stones contagious. Let us find out more about it.
The majority of the time, tonsil stones are at fault
Bacteria and other foreign substances, such as dead cells and mucus, may get stuck in your tonsils and cause an infection. If this occurs, debris may get attracted to one another.
This material crystallizes or hardens, forming tonsil stones. Individuals with chronic or recurrent tonsillitis have an increased chance of getting this condition.
Many individuals have little tonsil stones, but huge tonsil stones are quite uncommon.
Symptoms of Tonsil Stones
If you have tonsil stones in your mouth, you may have no symptoms. Large tonsil stones are often detected only using X-rays or computed tomography scans. Several of the symptoms and indicators include the following:
- Halitosis, or poor breath, is often the first indicator of tonsil stones, which develop when the tonsils become inflamed due to infection. In one research, patients with chronic tonsillitis had their breath analyzed for volatile sulfur compounds, indicating poor breath. The researchers discovered that these chemicals were present in abnormally high concentrations in 75% of the tested patients.
- It may be difficult to tell the difference between a tonsil stone and tonsillitis due to the inflammation in your throat. However, as a consequence of the tonsil stone, you may have pain or discomfort.
- A stone in your throat may cause a coughing episode.
- Because a tonsil stone’s size and position vary, swallowing food or liquids may be difficult or painful.
- Stones may develop in any location on the tonsil. Even if the stone is not directly in contact with the ear canal, neurological connections may cause discomfort in the ear.
- In addition, your tonsil may enlarge in size due to the inflammation and infection produced by a tonsil stone.
Detection of Tonsil Stones
Your doctor will often do a thorough physical examination to find tonsil stones. In addition, imaging studies, such as CT or MRI scans, may be necessary to locate them in the folds of your tonsils.
What You Should Know About Tonsil Stone Removal and Treatment
Numerous tonsil stones, particularly those that are asymptomatic, may not need medical intervention. It all depends on their size and danger level.
This kind of treatment is available:
- Antibiotics: Although medication may effectively treat tonsil stones, it has side effects and does not address the underlying issue.
- Surgeons are necessary to remove the tumor: Your doctor may also prescribe that you get your tonsil stones removed if they are very large or causing you difficulty.
- Tonsillectomy: To get rid of tonsil stones that have been hurting you for a long time, you may need to undergo surgical removal.
- Cryptanalysis: A laser or radiofrequency wand may be used to scar the tonsils to limit the risk of tonsil stones developing.